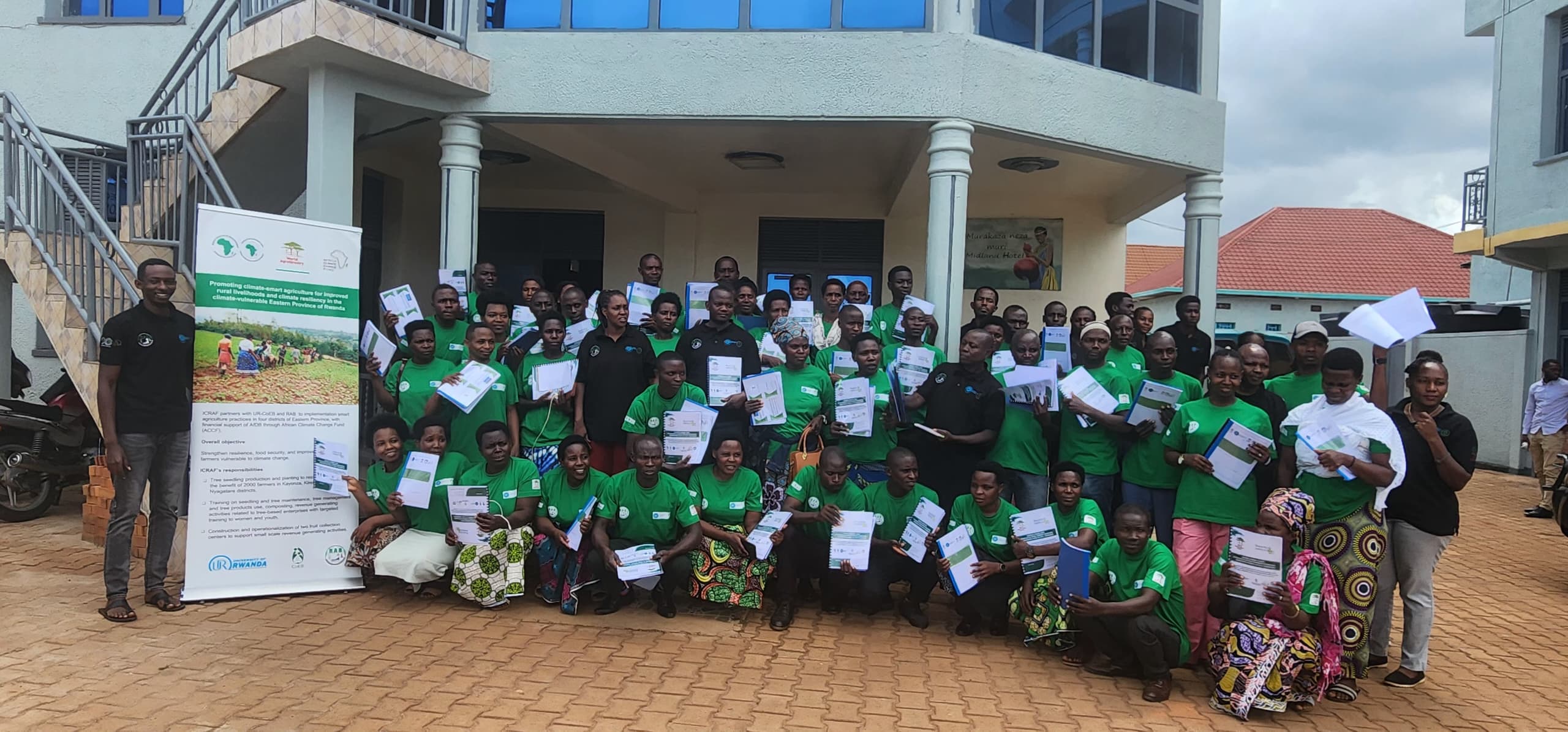
As part of the project “Promoting Climate-Smart Agriculture for Improved Rural Livelihoods and Climate Resiliency in the Climate-Vulnerable Eastern Province of Rwanda”, a series of targeted activities have been launched in Kirehe, Kayonza, Nyagatare, and Gatsibo districts. The project is implemented by the Center of Excellence in Biodiversity and Natural Resource Management at the University of Rwanda, the Rwanda Agriculture and Animal Resources Development Board, and the International Center for Research in Agroforestry.
The initiative aims to strengthen the resilience of rural communities by promoting climate-smart agricultural practices and supporting income-generating activities such as beekeeping. Between April and June 2025, two key capacity-building interventions were carried out under the project.
Supporting Beekeeping Cooperatives with Modern Techniques
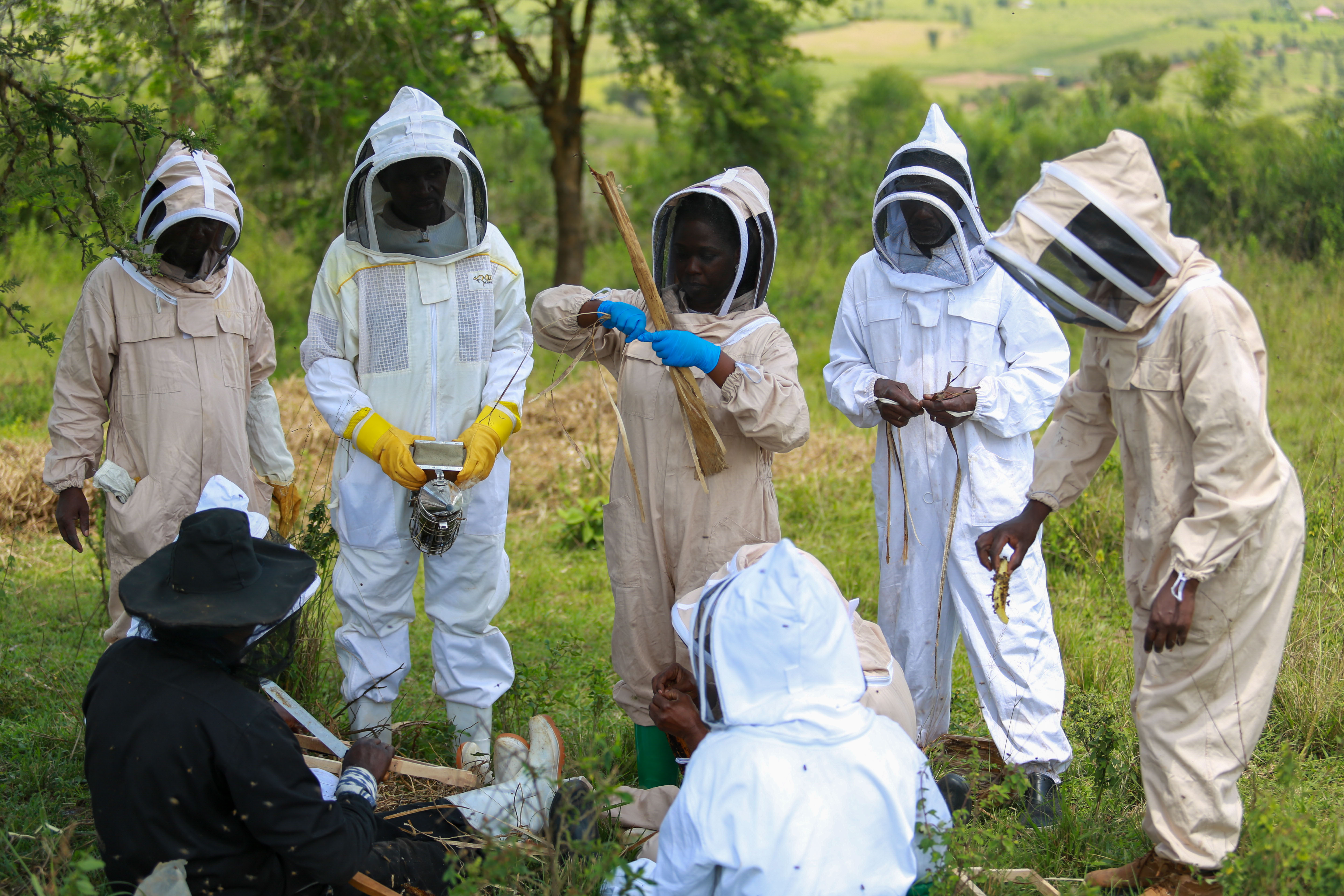
In May 2025, the project extended its support to six beekeeping cooperatives across Gatsibo, Kayonza, and Nyagatare, through hands-on training on modern beekeeping practices. A total of 146 participants (66 women and 80 men) were trained on transferring bee colonies from traditional hives to modern Langstroth hives and improving colony management.
Each cooperative received a full set of modern equipment—including queen excluders, smokers, honey extractors, pollen traps, and protective gloves. A critical part of the training focused on identifying and transferring the queen bee, reducing colony stress, and ensuring hive stability. Trainers demonstrated the process on-site at each apiary, ensuring farmers could replicate the techniques independently.
This beekeeping intervention aligns with Rwanda’s National Strategy for Transformation (NST2, 2024–2029), which identifies honey production as a priority export sector. By professionalizing smallholder beekeeping, the project enhances rural livelihoods while supporting biodiversity and sustainable land management.
Together, these activities reflect the project’s holistic approach to climate resilience—combining science-based agricultural planning with sustainable value chains to empower communities and ensure no one is left behind in the face of climate change.
Empowering Farmers with Weather and Climate Data
In April 2025, a four-day training was organized in Kayonza to equip 50 lead farmers, 23 men and 27 women, including 24 youth with practical skills in interpreting and applying meteorological data to farming decisions. Delivered in partnership with Meteo Rwanda, the training included interactive sessions and field visits to help participants understand weather patterns, plan agricultural activities, and respond more effectively to climate-related risks.
Farmers were also trained in how to access real-time forecasts using smartphones provided by the project. By strengthening the connection between farmers and the Rwanda Meteorological Agency, the activity helps ensure that climate information is used at the local level to enhance productivity and reduce vulnerability.